Services
- Home
- Services
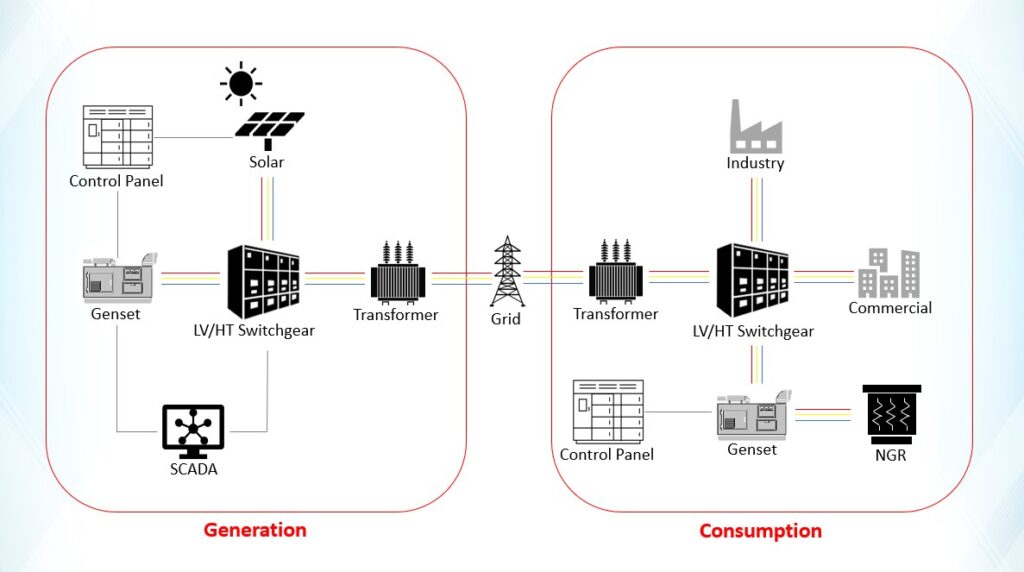
Power System Integration
Power system integration is the process of combining various energy sources, technologies, and infrastructure to create a unified, stable, and efficient electrical grid. This includes integrating renewable energy sources like solar into existing grids, managing intermittent generation with energy storage systems and demand response, and connecting regional or national grids for improved reliability and efficiency. Key challenges include managing the variability of renewable energy, maintaining grid stability, and addressing regulatory and cybersecurity concerns. Ultimately, power system integration promotes reliability, cost efficiency, and environmental sustainability by optimizing resource use and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Installation & Commissioning
Installation and commissioning are critical phases in the deployment of electrical systems, equipment, or infrastructure, ensuring that everything operates as intended and meets safety, performance, and regulatory standards.
Installation refers to the process of setting up electrical equipment, systems, and components at the designated site. This involves reviewing design specifications, preparing the site, and ensuring that all necessary tools, materials, and permits are available. Installing components like transformers, switchgear, control panels, cables, and renewable energy systems as per design plans and technical standards. Properly connecting electrical circuits, ensuring that wiring follows safety protocols, and confirming the installation of grounding systems. Ensuring that all installations meet local codes and standards for electrical safety.
Commissioning is the process of testing and verifying the functionality, performance, and safety of the installed systems to ensure they work as intended. It typically includes: Testing, System Calibration, Load Testing, Fine tuning & Final Adjustments etc. Proper execution during these phases minimizes future operational issues and maximizes the longevity and performance of the system.


Inspection & troubleshooting
Inspection and troubleshooting are essential tasks in maintaining the reliability and efficiency of electrical systems. It helps to identify, diagnose, and resolve issues, ensuring that systems operate safely and optimally.
Inspection involves a detailed examination of electrical equipment and systems to ensure they are functioning properly and in compliance with safety standards. It includes Visual Inspections Routine Testing, Preventive Maintenance & Safety Checks
Troubleshooting is the process of diagnosing and resolving issues in electrical systems. It includes Fault Diagnosis, Systematic Testing, Isolating the Issue, Repair or Replacement & Post-Troubleshooting Tests.
Both inspection and troubleshooting are crucial for maintaining the integrity, performance, and safety of electrical systems, preventing costly downtime, and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
FAT & SAT
Factory Acceptance Test (FAT) and Site Acceptance Test (SAT) are crucial testing phases in the deployment of electrical systems or equipment. FAT is conducted at the manufacturer’s facility before the system is shipped to the site, ensuring it meets design specifications, functions correctly, and complies with safety standards under controlled conditions. It includes testing individual components, system integration, and performance under simulated loads.
SAT is conducted at the installation site and verifies that the system operates as intended in the actual environment, under real-world conditions. It focuses on checking installation accuracy, system functionality, environmental compatibility, integration with existing infrastructure, and final calibration. Both tests ensure that the system is fully operational, compliant with standards, and ready for service.
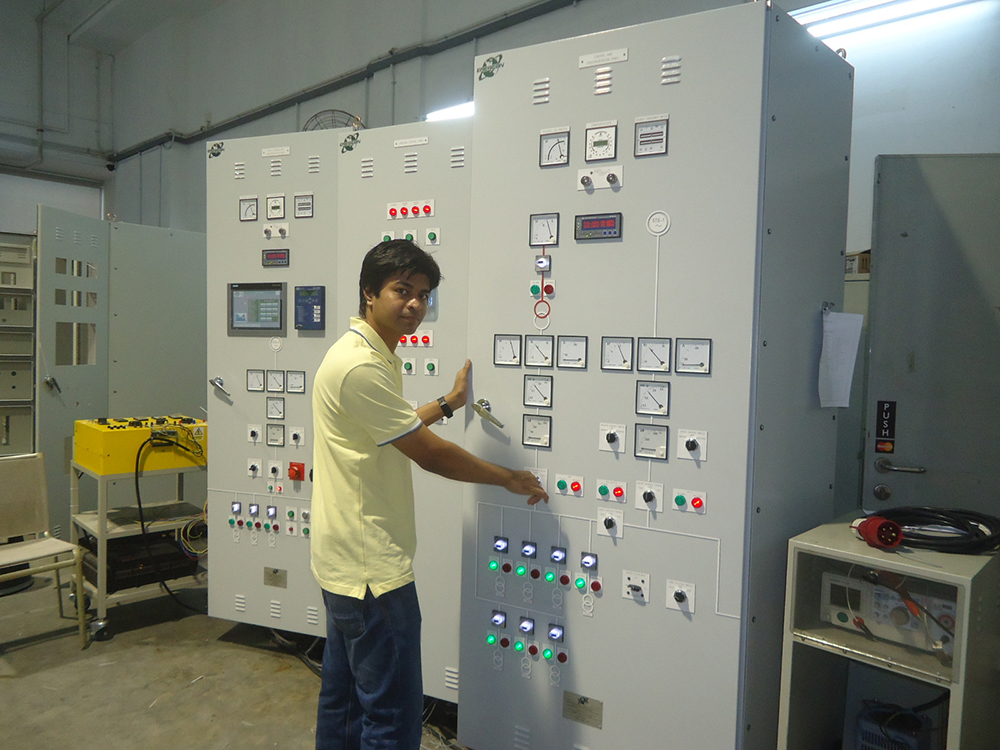
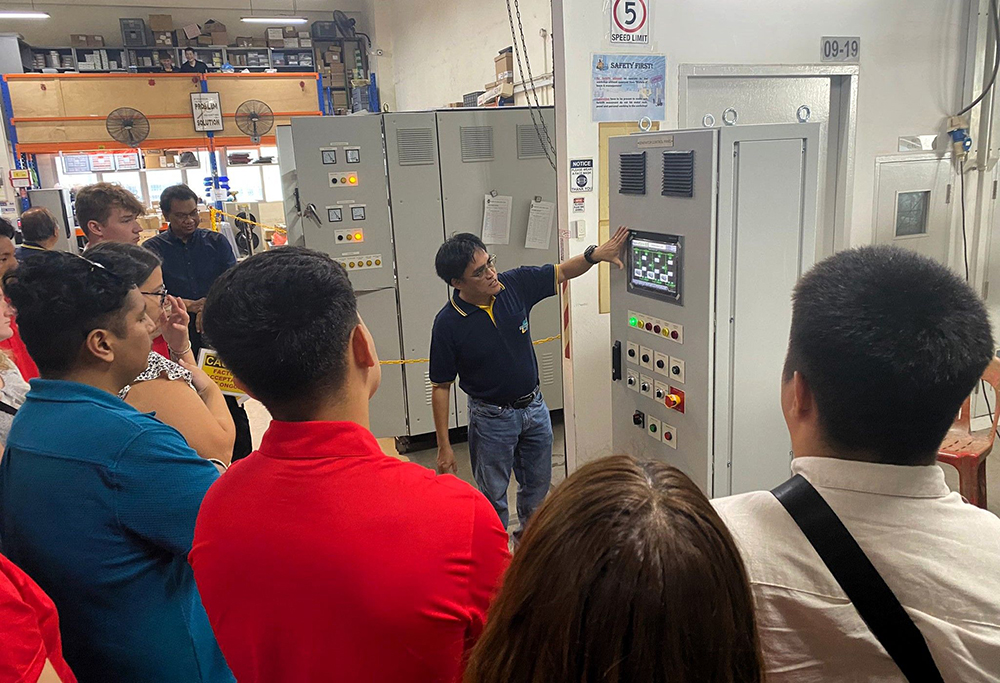


Customer Training
Customer training is to train clients on how to effectively operate, maintain, and troubleshoot equipment or systems, ensuring they can use it safely and efficiently. It includes instruction on system operation, routine maintenance tasks, troubleshooting common issues, and safety protocols, such as emergency shutdown procedures. Additionally, customers are trained on using control panels, dashboards, and monitoring tools. The training is often delivered through hands-on sessions, manuals, video tutorials, and online resources, helping to enhance operational efficiency, minimize downtime, and reduce reliance on technical support, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and system longevity.
Relay Coordination
Relay coordination is to setting up protective relays in an electrical power system to ensure they operate in a coordinated manner during faults, protecting equipment and minimizing system disruptions. The goal is to determine the optimal settings for each relay, such as time delays and trip settings, so that when a fault occurs, the relay closest to the fault operates first, isolating the problem without unnecessarily interrupting power to other areas of the system. This involves careful analysis of the protection scheme, including selecting appropriate relay types and setting their characteristics based on factors like fault current, system configuration, and coordination with other protective devices. Effective relay coordination ensures that the protection system operates selectively, maintaining the stability and reliability of the overall power network while preventing widespread outages.
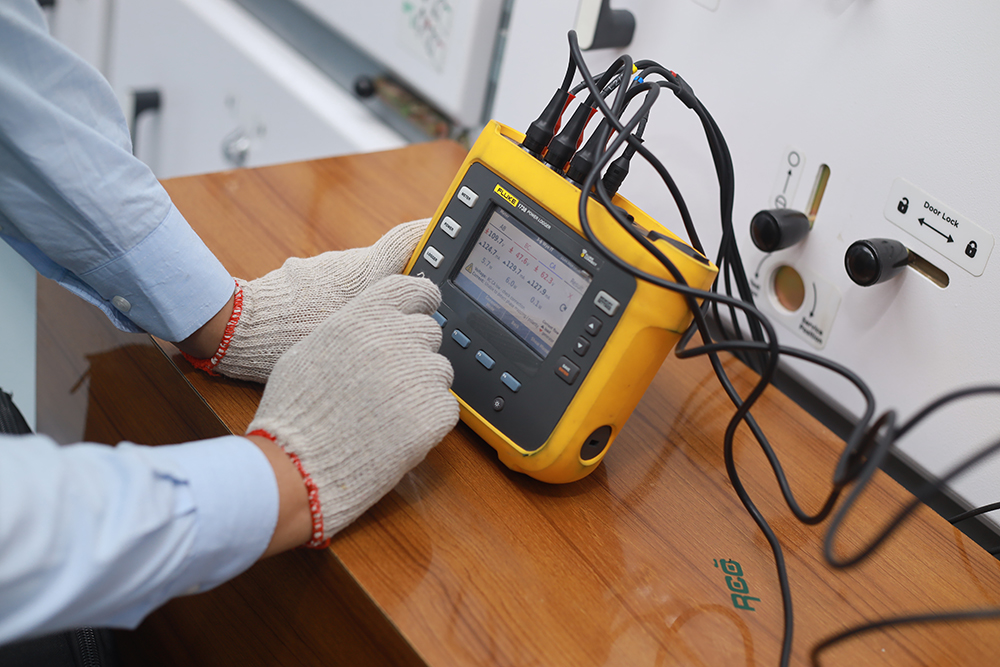
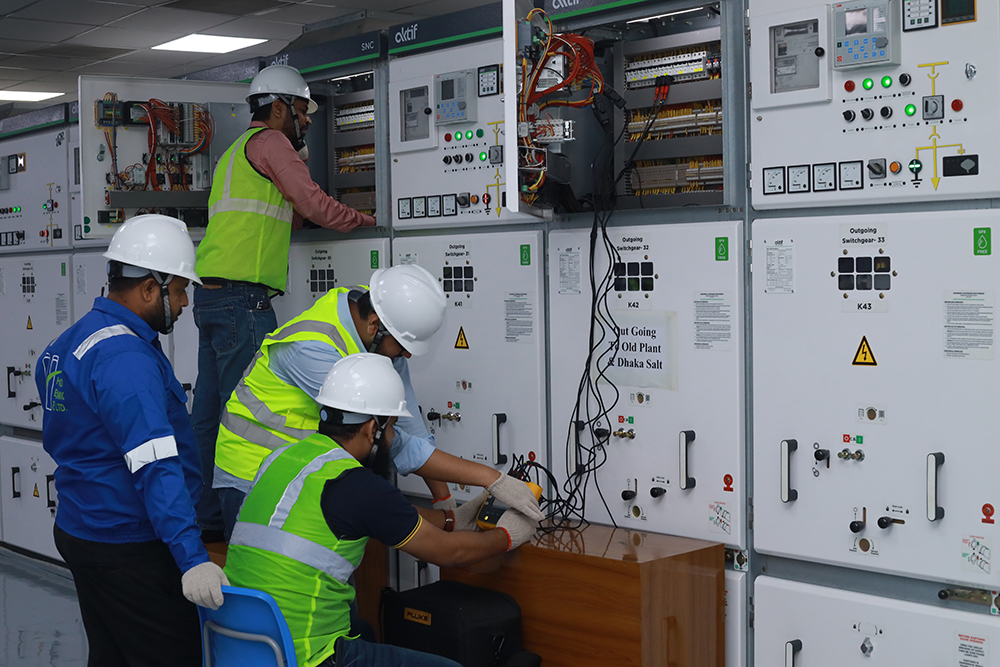


Annual Maintenance
Annual maintenance refers to the scheduled, regular servicing and inspection of equipment, systems, or infrastructure to ensure they remain in optimal condition, operate efficiently, and meet safety standards over time. For electrical systems, this typically includes tasks like checking and cleaning components (e.g., transformers, switchgear, circuit breakers), testing protective devices and relays, inspecting wiring and connections for wear or damage, calibrating control systems, and verifying safety protocols. Additionally, annual maintenance may involve updating software, replacing worn-out parts, and performing system diagnostics to identify potential issues before they lead to failures. The goal of annual maintenance is to minimize downtime, extend the lifespan of equipment, improve performance, and ensure compliance with industry regulations and safety standards.
Consultancy
Consultancy in the context of electrical systems or engineering refers to professional services provided by experts to guide clients in planning, designing, implementing, optimizing, and maintaining their electrical infrastructure or projects. Consultants offer specialized advice based on their expertise, helping clients solve complex problems, improve system efficiency, and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. Consultancy involve project management, technical support, ensuring that projects are executed smoothly, on time, and within budget, ultimately enhancing the client’s operational performance and safety. This may include,
- System Design and Planning
- Feasibility Studies and Risk Assessments
- Energy Audits and Efficiency Improvements
- Relay Coordination and Protection System Design
- Troubleshooting and System Optimization
- Training and Support
Consultancy add significant value by helping clients make informed decisions, solve complex engineering problems, and improve the efficiency, safety, and sustainability of their electrical systems. Their expertise ensures that projects are executed effectively, risks are minimized, and systems operate optimally over the long term.
